Last time, we were introduced to the design and operational considerations of offshore structures. Now, we will take look at the different types in existence today. Before we go into that, take a recap of the previous article here. Also, you might want to see how fierce the environmental conditions can be in this video given below:
Broadly, offshore structures maybe of two types:
Surveillance of the sea-bed and that of the underlying rocks helps in the development of the strategic sites for the optimum extraction of the resources. Furthermore, the oceanographic and climatic conditions around that region are assessed. Then the topographic conditions pertaining to that particular region along with the critical risk factors probable to the given sea-state gives the outline for the apt installation for the site. The offshore structures maybe mobilized from one site to another, may be erected after compilation of the raw materials and parts or maybe made from scratch at the purported site itself depending on its nature.
Broadly, offshore structures maybe of two types:
- Floating - These offshore platforms are floating in free surface and are movable from one location to another. Examples include semi-submersibles, SPAR platforms, Floating-leg platforms, drill-ships, FPSOs(Floating Production, Storage and Offloading systems)
- Fixed Platforms: They are immobile and fixed permanently to one place. These sorts of offshore units have greater strength and relative durability as compared to floating ones. These are operationally irreversible as once installed they cannot be relocated . Examples are Concrete/Gravity Platforms, Jacket Platforms,Tension-leg platforms(TLPs), Jack-Up Rigs etc.
 |
| Fig.1:Image of a deep-sea offshore installation (Courtesy: www.nyborgfan.com/) |
As these offshore structures are high-budget, heavy-duty and long-term projects, umpteen care is taken to ensure its livability in hostile sea state and its long term life span.
Jacket Platforms
These platforms are quite common and comprise of an outer jacket-like structure of welded tubular steel. Steel jackets are vertical sections made of tubular steel members, and are usually piled into the seabed. The pipes are about 1 to 2 m in diameter and have a maximum penetration of about 100 m. They weigh about 20000 tonnes. This external steel jacket has many functions ranging from stability and supporting the entire structure to protecting the internal piping and drill equipment from external disturbances.
Design Parameters
These steel jackets have tapering, truss-like structure with high strength, durability and fatigue resistance.Loading and life cycle apart from diameter, penetration, thickness and spacing are taken into account.
- In a typical design , the cross-sectional dimensions are about 70*65 at the seabed and 56*30 at the top.
- They have capacities of resisting forces up to 50 MN in compression and 10 MN in tension and has a large vulnerability to lateral loads like expansion and hydrodynamic stresses.
- They also have a maximum permissible overturning moment up to 10 GN.m in most cases.
One point to ponder upon in jacket structure is the protection of the steel from rust and corrosion, a "disease" of all marine vehicles and structures which is principally to be taken care of . This can be done up to a certain extent by using high-grade "stain free" steel and by repeated cathodic protection.
Jack-Up Rigs
Jack-Up drilling rigs are a type of self-elevating, mobile platform capable of raising the hull part which is obviously buoyant above the sea level and penetrating its steel legs into the sea-bed for support for deep sea drilling operations. The name "jack-up" is derived from versatile nature of the legs or jacks which can be suitably jacked above or below the hull accordingly when not in operation and when in operation.
These Legs maybe piled into the sea-bed or maybe placed on large footings for better grip and stability. There maybe three or four legs for jacking up the buoyant hull above the sealevel for operations. After a stipulated time period after termination of the operations at a place, the legs are dismantled from the sea floor and are jacked above the hull and the entire unit is mobilized to another destination maybe to some jetty/port or to another drilling site. They are not self-propelled and usually depend on tugs of Heavy Lift Ships for towing from one place to another.
Well when and where can jack up rigs be used? The answer IS that they maybe used in shallow waters as pre-operation and post-operation mantling and dismantling of the jack ups are very bleakly feasible in deeper waters. The steel legs are of high strength HSS steel and are designed to confront wave dynamics even in rough seas up to a certain limit. Care must be taken for their maintenance in terms of corrosion, fatigue, stresses. In case of sea or external parameters going beyond the tolerance level, these are immediately "jacked up" and are shifted to safer locations or kept in a safe nonoperational, dormant mode.
Jack -Up rigs are used specifically for oil well drilling purposes and has limited or no storage capacity. Storage or bulk transport may be through oil tankers or the multi-purpose FPSOs (Floating Production, Storage and Offloading Units).
The rig consists of narrow, flexible (compliant) towers and a piled foundation supporting a conventional deck for drilling and production operations. They are mainly operated in depths upto 1500 to 3000 feet. They inherently have a frequency lower than the natural frequency of the waves, such that with the emergence of any wave disturbance can make it oscillate with a resultant frequency safer for the loads and eradicate the probability of any resonating conditions. They work on a principle of de-amplification of waves dissipating the energy responsible for creating greater mayhem. Hence they are applicable for high tide or even the worst sea conditions.The lower part of the frame depends on the pilings and can penetrate hundreds of feet below the mud line.
 |
Fig.3: Basic Components of a Steel Jacket Offshore
Structure (Copyright: Maersk)
|
Concrete Platforms/Gravity Platforms
Concrete Structures are purely composed of concrete and is considered the safest mode of offshore industrial operations. They maybe directly fixed or molded to the sea floor on a permanent basis or maybe floating.
Fixed ones are also known as Gravity-based structures or the Caisson type. The entire structure is based on a submerged island-like solid structure which may serve as a foundation structure as well as storage or oil or other by-products. The entire load of the structure acts directly on the subsequent layers of the sea-bed eradicating problems even of the extreme wave disturbances or seafloor scour. On the other hand the floating ones are freely float-able and has six degrees of freedom under a proper mooring system.
Some designs of these concrete structures are Condeep, ANDOC, Doris and so on. The design parameters are guided by the number of supporting columns and the diameter of the legs. Constructing is a tedious process where the entire structure or its components are towed and assembled with proper ballasting and de-ballasting measures. They have almost negligible maintenance and high durability. Can be also used for greater depths.
Compliant Towers
Whenever the word "compliant" comes to our mind we mean a sense of complying or yielding. These are tall, slender, single isolated structures with high slenderness ratio.
They are comprised of specialized flex tubes of 2 to 7 metres in diameter comprising the space-time frame-like truss with high degrees of flexibility and can withstand high amounts of lateral loads up to 10 feet due to waves or oceanic disturbances.
The rig consists of narrow, flexible (compliant) towers and a piled foundation supporting a conventional deck for drilling and production operations. They are mainly operated in depths upto 1500 to 3000 feet. They inherently have a frequency lower than the natural frequency of the waves, such that with the emergence of any wave disturbance can make it oscillate with a resultant frequency safer for the loads and eradicate the probability of any resonating conditions. They work on a principle of de-amplification of waves dissipating the energy responsible for creating greater mayhem. Hence they are applicable for high tide or even the worst sea conditions.The lower part of the frame depends on the pilings and can penetrate hundreds of feet below the mud line.
 |
| Fig.6: Different Compliant Structures through the years (Courtesy: www.atp.nist.gov/) |
Tension-Leg platforms
These are floating facilities which stay afloat and remain in position with the help of specialized steel tubes called tethers or tendons. These are nothing but the supporting legs of the floating platform which by the virtue of their upward tension takes care of the position, loading and the functionality of the extraction system. For all such tension leg platforms there is not much vertical oscillatory motion of the platform how rough the sea conditions or the average wave height may be. This facilitates in tying with the wellheads and the piping system for extraction of oil without much distortion. for all such systems there is always an additional buoyant force which keeps the platform afloat. Thus for all such installations,
Tension =Buoyancy - Weight
Here topside facilities and the basic parameters like the number of risers have to be fixed at pre-design stage. Generally the platform is manufactured on the shore and is towed to the desired location with the help of tugs. This structure is apt for depths up to 1200 metres and has limited or no storage facility. As of common usage, these have a high maintenance and surveillance cost of the tethers and under unavoidable circumstances the structure may be prone to irreversible damage.
Fig. 7: Structure of a typical tension-leg platfrom (Courtesy: www.slideshare.com)
Semi-Submersible
They are floating installations which rest on four or six pillar-like legs called columns with a equal weight distribution on each. These columns or legs are in turn attached to large basements called pontoons floating on the water surface. These pontoons may be ballasted or de-ballasted accordingly on and off operations. Often these pontoons delve deeper under the water surface and maintain the buoyancy and position of the floating system. There is always a greater draft. Thereafter the operational deck is kept well aloof from the wave disturbance or the rough seas.However due to small waterplane area the structure is sensitive to load variations and must be trimmed accordingly. They by the virtue of their equivalent weight distribution and a high draft, it has a greater stability than normal ships. The number of legs, pontoon design , the situation of the risers and drill equipment are decided at pre-design stage. They are generally instrumental in Ultra-deep waters where the fixed structures pose a problem. Their position is maintained generally by a catenary mooring system or sometimes in modern structures by Dynamic :Positioning System. These structures are gigantic and may be towed from one location to another by the virtue of a kind of ships called Heavy Lift ships.
SPARS
These have a large diameter cylindrical deck supporting the main deck .They are generally developed as oil platforms for deeper waters as an alternative to the conventional systems. Most of the drilling and oil extraction equipment are situated within them. The inside part of the cylindrical truss is filled with some material denser than the sea-water to lower down the centre of gravity and hence maintain the vertical stability of the structure. The deep draft design of spars makes them less affected by wind, wave and currents and allows for both dry tree and subsea production. The cylindrical structure is surrounded by helical strakes to avoid vortex-induced motion.
The first prototype of the SPAR Platform was Neptune laid off the US coast in 1997.
There are basically three types of spars, namely, truss spar, classic spar and cell spar.
It is generally equipped with taut catenary mooring and the heave natural period is generally below 30 seconds. Generally , the spar is employed for depths up to 2300 m. The number of risers is restricted generally due to the limited space of the core cylinder. These are highly stable and hence are negligible unaffected even on adverse sea conditions or sharp environmental vagaries.
Fig. 10: A typical deep sea SPAR Platform (Courtesy:www.maritimeconnector.com)
FPSOs
FPSOs stand for Floating, Production, Storage and Offloading Systems. It is a specialized vessel for the purpose of offloading, processing, storage, distribution of oil and other hydrocarbon resources. One important point to wonder is that these installations does not have anything to do with the extraction purposes and can be merely reckoned as a carrier with specialization. These vessels eradicate the need of long pipelines for transfer of oil and petroleum to the shore. FPSOs are preferred in frontier offshore regions as they are easy to install, and do not require a local pipeline infrastructure to export oil. FPSOs can be a conversion of an oil tanker or can be a vessel built specially for the application. A vessel used only to store oil (without processing it) is referred to as a floating storage and offloading vessel (FSO). These can operate extensively in remote and deep waters and also in marginal wells where fixed platform or piping is technically or economically not feasible.
In majority of the cases the vessel may be buoyed to a vicinal drilling platform. Also the oil or other petroleum products maybe transported to the mainland by pipelines or by a conventional mooring system. The vessel may be fixed in a particular position by mooring lines or by a dynamic positioning system (DPS).
Fig.11: The ongoing operations to an FPSO and the production process
 |
| Fig.12: Floating production storage and offloading unit (Courtesy: www.alibaba.com) |
These ships have an integral storage capability inside their voluminous hull and have a calculated freeboard and draught. They are operational in adverse weather and have a high maintenance cost.
Drill ships
It is a mobile offshore installation akin to a
ship which is specialized for exploration and drilling of oil and gas resources
more specifically for scientific exploratory purposes. Mostly, it is used for
deep and ultra deep applications involving exploratory and drilling
purposes. The first drillship was the CUSS I, designed by Robert F. Bauer of Global Marine
in 1955. The CUSS I had drilled in 400 feet deep waters by 1957.Apart from
regular drilling purposes, the drillship may also be used for maintenance
and surveillance purposes such as casing and tubing installation, subsea tree
installations or wellhead capping. Drillships though expensive and of high
precision in operating and maintenance, is often believed to be the most
proficient mode of offshore technology trend where like any conventional ship,
it can be transferred from one place to another anytime and that too without
the use of any tugs , heavy lift ships or any other towing system. However a
mandatory mooring system should be kept or a DPS positioning system
should be employed. Generally, underneath the derrick through the hull is
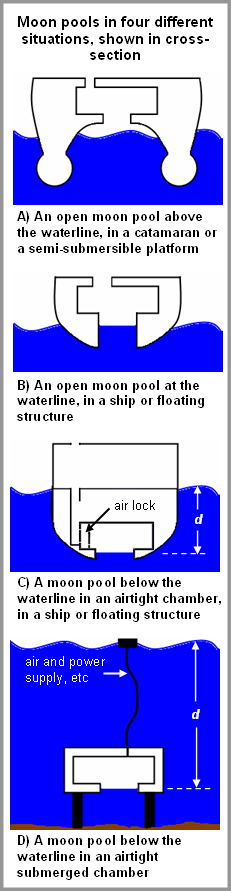
the moon pool which connects the deck to the sea directly. Sounds pretty
interesting, isn't it ? The moonpool is generally an opening of
the deck floor with the water in any marine research
vessel, drillship, sometimes icebreakers, diving support vessel for easy
exposure to the underwater environment or for the easy steup of the drilling
equipment as done here. Generally moonpools are situated in four different
positions, above the waterline, at the waterline, underneath the waterline or
deep submerged depending upon the requirements, the vehicle or the design. So,
for a drillship the moonpool provides easy accessibility for the drill
equipment or manpower for the purpose of maintenance of the drill equipment or
underwater survey. However immense care has to be taken during the design stage
to ensure the moon pool compensates the loss of strength in the deck or hull,
maintain stability and trim and avoid flooding or leakage.
Fig. 13: Different types of moonpools (Courtesy: www.wikipedia.com)
A simple way to understand what a drillship is to do in order to drill, a marine riser is lowered from the drillship to the seabed with a blowout preventer (BOP) at the bottom that connects to the wellhead. All this is done through the moonpool intricate to the hull. Drillships also have their own storage and processing system . However, in terms of positioning and stagnancy during drilling operations, the semi-submersibles have an upper hand.
 |
| Fig. 14: A TIGER Series Drillship (Courtesy: ) |
This was all about the common types of offshore structures in existence today.LSD
Article By: Subhodeep Ghosh








This is an extremely interesting post! Well Done!
ReplyDelete
ReplyDeleteReally awesome blog. Your blog is really useful for me. Thanks for sharing this informative blog. Keep update your blog.
Turnkey Office Interior Services